The Future of B2B Climate Tech: Sustainability Enterprise Software
For those who have been following the major venture capital investment trends over the previous year, climate tech is a vertical that has undoubtedly been pushed to the forefront of not only investment, but public discourse.
And for good reason. In 2021 alone, the US experienced 20 major climate disasters that cost $145 billion. In late February of this year, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) published an alarming report pleading for a collective call to action to mitigate the detrimental effects of climate change. Climate tech is driving the reversal of this damage.
Corporations globally are engaging in the race to decarbonization. Corporate net zero initiatives have been intensified by consumer demand shifts, notably amongst Gen Z and Millennials, with recent studies indicating that over 62% of consumers in these demographics prefer sustainable brands and are willing to spend 10% more on such products/services. 85% of companies are concerned about reducing their carbon footprint, but only 9% can exhaustively and accurately measure their emissions and 11% have been able to decarbonize to desired target levels.
Organizations are in need of enterprise software solutions that can accurately measure, monitor and reduce carbon emissions. At FFF, we believe that there is a need for startups building cloud-based sustainability enterprise software. To improve outcomes we first need to measure and track, and winners will ultimately need to exhaustively measure emissions in real-time, automate data collection and extrapolation, simulate future impact, and customize carbon reduction strategies, among other capabilities.
Background and Terminology
First, let’s dive into the basics: Clean tech, widely considered to be the predecessor to climate tech, focuses on enhancing production, while minimizing environmental impact. Climate tech, however, includes the technology and business models that specifically mitigate climate change. Clean Energy Ventures defines and further explains the differences between the two here.
We have seen green investment cycles come and go for several decades, the most recent being the “clean tech bubble”, which burst during the 2008 financial crisis, leaving investors badly burned. Despite investor flashbacks to this era, in recent years, venture investment in climate tech has soared. Climate tech VC investment grew from $17 billion in 2020 to $40 billion in 2021, and its median market size is estimated to be $46 trillion as of 2021.
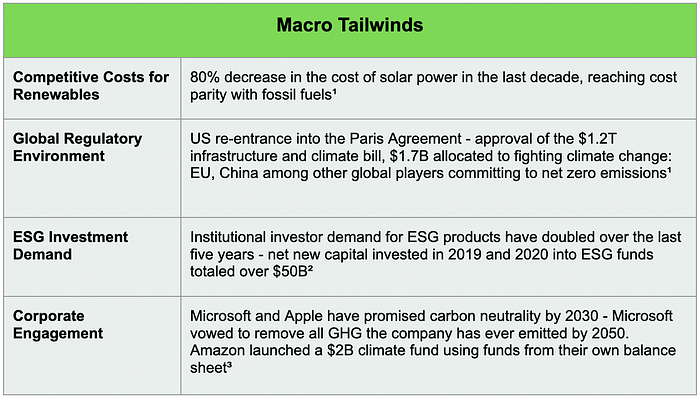
Sustainability Opportunity For Businesses
On a global level, we have understood for some time why mitigating climate change is important for our earth. Yet it wasn’t until recent years that companies began pledging carbon neutrality by the not-so-distant future. Why now?
Employee Demand
83% of employees believe their current employers are not doing enough to mitigate climate change. 65% are more likely to work for companies with aggressive sustainability policies.
Competition
Consumers and trade partners increasingly want to interact/align with companies with strong track records of environmental and social responsibility.
Investors
Investors want to invest in companies that are committed to progress and the future. ESG fund managers have increasingly stricter vetting requirements when considering companies for investment.
Risk Management
Impending corporate emissions disclosure regulations and increased operational risk from climate-related disruptions have corporations scrambling to adopt solutions that help them manage their sustainability data and enhance visibility into their operations.
What Are We Seeing Today?
There are a number of trending B2B climate tech verticals that companies, across industries, have been integrating into their operations, which raises the question: which business models will both move the needle on climate change mitigation and sustainably gain traction for the foreseeable future?
Trending B2B Climate Tech Verticals
Consumer Accountability: Green e-commerce APIs that help individual consumers quantify and reduce their carbon footprints. These technologies provide users with detailed emissions data with every purchase or transaction. Given what we know about some of the Earth’s largest carbon emitters, consumer accountability solutions will likely not be enough to move the needle on reaching global net zero goals. Gone are the days of shifting the climate change burden from companies to individuals, as the largest emitters are at the corporate level. Example of a leading female founded startup in this vertical: Joro
Carbon Offset Purchasing: The practice of “offsetting” existing carbon emissions by avoiding them elsewhere, typically through third party projects. These carbon offset purchases typically support re-forestation projects, though they do not remove the existing carbon corporations have emitted into the atmosphere. The carbon offset market continues to be scrutinized by climate advocates and investors everywhere, due to the lack of transparency, regulation and verification of the impact of these projects. With Fed promises of imminent interest rate hikes and investor fears of extreme market corrections, the carbon offset market will likely suffer dramatically as corporations reassess their cash flow needs. Example of a leading female founded startup in this vertical: Supercritical
Carbon Removal: Though typically confused with carbon offsetting, carbon capture and removal technology completely removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and is viewed by some climate investors as the future of climate change mitigation. These technologies are the most promising solution that will enable companies to truly reach net zero; however, the technology is not advanced and scalable enough to be profitable at the commercial level. That being said, experts estimate these technologies will reach maturity within the next decade. Example of a leading female founded startup in this vertical: Remora
Where FFF Sees The Investment Opportunity
Sustainability Enterprise Software: FFF sees opportunity in platforms that help companies quantify, understand and reduce carbon emissions throughout their respective value chains. Enterprises of all sizes, but especially medium to large-sized companies, not only struggle with the ability to aggregate emissions and general sustainability data, but they also have difficulty understanding how to extract business value from such data. In fact, advanced technologies such as AI/ML have the potential to help corporations, as a whole, generate between $1-$3 trillion in value through cost reductions and increased revenues by 2030. Existing sustainability enterprise software solutions largely lack the capabilities to exhaustively collect, automate and extrapolate emissions data, while also providing strategic value to enterprise customers. Examples of leading female founded startups in this vertical: Unravel Carbon, Ecocrumb, Planet FWD, and GoodStats.
What Will The Future Successful Startups In This Space Look Like?
While there are many startups entering this vertical, we believe there are several specific capabilities and characteristics that will differentiate the future successful startup within the space.
Exhaustive emissions measurement
In order to achieve net zero, companies need to understand their corporate emissions data both exhaustively and at a granular level.
Real-time tracking
Corporate emissions data collection and analysis monitored on a real-time basis to ensure companies can track the progress of decarbonization plans.
Automated data collection and extrapolation
Fully automated data collection replaces painstaking manual collection. Machine learning technology identifies patterns and extrapolates emissions sources throughout each step of the value chain.
Supply chain traceability
Blockchain and digital twin technology enable accurate measurement of supply chain emissions, process efficiency through enhanced visibility, and safety of corporate data.
Future impact simulations
AI technology that enables carbon reduction planning scenario simulation and future impact measurement to help enterprises set and meet reasonable emissions targets while also maintaining or increasing profitability.
Fully customized decarbonization strategies
Development of carefully curated carbon reduction strategies, monitored in real-time, which align company emissions goals with time and budgetary constraints.
Cloud-based platform
User-friendly, cloud-based platform that aggregates all emissions data, including performance tracking and benchmarking, updated in real-time so users can easily understand and monitor emissions.
Aggregated benchmark reporting
Creation of comprehensive emissions reduction reports following GHG protocol, including internal and external benchmark data, for distribution to company investors and end users.
What technologies will these startups be using?
- AI/ML: Measuring future impact through AI-driven simulations, making accurate inferences about emissions sources through data analysis.
- Blockchain: Ensures safety of private company data needed to analyze emissions; offers accurate visibility into company operations, including supply chain management.
- Digital Twin: Monitor operations throughout the value chain to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, bridging the gap between physical and digital asset data.
- Cloud: Automated data aggregation across digital enterprise platforms, real-time project performance updates and impact on profitability, accessible through an easy-to-use platform.
Current Momentum
Notable Acquisitions
In recent years an increasing number of companies have acquired early-stage sustainability enterprise software startups and integrated the technology into their portfolios and operations.
Planetly: Berlin-based, carbon footprint management platform, founded in 2020, was acquired in December 2021 by OneTrust, a governance and privacy management platform recently valued at $7B.
ecobee: Canadian smart home energy management software company, founded in 2007, was acquired in December 2021 by Generac Power Systems, a publicly traded power generation equipment manufacturer, for $730M.
Accuvio: Ireland-based sustainability data software company, founded in 2009, was acquired in August 2021 by Diligent, a corporate governance software platform, through an LBO.
The Climate Service (TCS): North Carolina-based climate risk analytics company, founded in 2017, was acquired in January 2022 by S&P Global.
Headwinds for Broader Adoption
We know why sustainability is important for our planet, so why is broader integration of these enterprise solutions so hard?
- According to a recent BCG research report, 45% of companies are limited by time and budgetary constraints and 32% do not feel incentivized by the company to adopt such comprehensive measures.
- Lack of US corporate regulatory standards requiring corporate emissions disclosures disincentivizes companies to accurately report emissions.
- Silver Lining? Climate regulations in the EU are priming the world for corporate emission disclosure laws. In the US, the democratic majority SEC has recently sought more of an active role with regard to sustainability regulations and have recently drafted a new law that may require corporations to disclose emissions throughout the value chain, including those from suppliers and trade partners.
- Apart from regulatory promises at the federal level, some states and local governments have enacted emissions laws and offered clean energy tax incentives, urging a consumer shift towards more sustainable service providers.
Key Takeaways
- Climate Tech: $46T market size estimate
- 85% of companies are concerned about reducing their carbon footprint, but only 9% can exhaustively and accurately measure their emissions and 11% have been able to decarbonize to desired target levels.
- Corporations have been facing heightened pressures from consumers, employees, trade partners, investors and impending federal legislation to get a better handle on their GHG emissions, throughout the value chain.
- Existing enterprise solutions lack the advanced technologies necessary to exhaustively collect, measure and track corporate emissions and/or develop customized carbon reduction solutions that can be monitored in real-time.
- The future is cloud-based sustainability enterprise software that exhaustively measures emissions in real-time, automates data collection and extrapolation, offers supply chain traceability, simulates future impact, customizes carbon reduction strategies and produces aggregated benchmark reporting.
- As US emissions regulations loom on the horizon, corporate demand for sustainability enterprise software will boom.
As we know, climate change is a critical issue with irreversible environmental, economic, political, social and health-related ramifications. While the road to global net zero will be difficult, we have been inspired by the impressive founders building in the space and look forward to continuing to monitor and support future innovation.
Written by: Rebecca Mandel, MBA @ NYU Stern

